Orakl Network

Introduction
Orakl Network is a decentralized oracle network that allows smart contracts to securely access off-chain data and other resources. It prides itself in being a native token oracle that provides Data Feed, VRF, Request-Response and Proof of Reserve solutions.
With Orakl Network, users can source for randomness that is unpredictable and unbiased in their smart contracts. Orakl Network Verifiable Random Function (VRF) allows smart contracts to generate verifiably random values, which can be used in various dApps that require randomness. Orakl Network provides developers access to the VRF services through two different account types, namely: Permanent Account or Temporary Account.
In this tutorial, you will utilize the VRF functionality from Orakl Network to request for random words from inside of your smart contract.
Prerequisites
- Kaia Wallet
- Remix IDE
- Kaia Plugin on Remix
- Test KAIA from Faucet
Getting Started
In the following steps, you will request for a random word in your smart contract using Orakl Network. Let's get started!
Step 1: Initialize Contract State Variables
In this step, we will define the cosumer contract and initialize the state variables needed for our contract functionality. Our consumer contract is dependent on VRFConsumerBase contract from which we inherit, and IVRFCoordinator interface that is used for calls to VRFCoordinator contract. Next, we define sRandomWord variable which we use to store the random word result and the sOwner variable which is used inside of onlyOwner modifier.
pragma solidity ^0.8.16;import { VRFConsumerBase } from "@bisonai/orakl-contracts/src/v0.1/VRFConsumerBase.sol";import { IVRFCoordinator } from "@bisonai/orakl-contracts/src/v0.1/interfaces/IVRFCoordinator.sol";contract VRFConsumer is VRFConsumerBase { uint256 public sRandomWord; address private sOwner; error OnlyOwner(address notOwner); modifier onlyOwner() { if (msg.sender != sOwner) { revert OnlyOwner(msg.sender); } _; }
Step 2: Initialize VRF Coordinator
To request for random words in your smart contract, you need to initialize the VRFCoordinator smart contract. It is recommended to bond VRFCoordinator interface with VRFCoordinator address supplied through a constructor parameter, and use it for random word requests (requestRandomWords). The VRFCoordinator contract is deployed both on Kaia Kairos 0xDA8c0A00A372503aa6EC80f9b29Cc97C454bE499 and Kaia Mainnet 0x3F247f70DC083A2907B8E76635986fd09AA80EFb.
IVRFCoordinator COORDINATOR; constructor(address coordinator) VRFConsumerBase(coordinator) { COORDINATOR = IVRFCoordinator(coordinator); sOwner = msg.sender; }
Step 3: Request Random Words with Temporary Account
To request random words with a temporary account, users need to send $KAIA together with a call using value property.
function requestRandomWordsDirect( bytes32 keyHash, uint32 callbackGasLimit, uint32 numWords, address refundRecipient ) public payable onlyOwner returns (uint256 requestId) { requestId = COORDINATOR.requestRandomWords{value: msg.value}( keyHash, callbackGasLimit, numWords, refundRecipient ); }
This function calls the requestRandomWords() function defined in COORDINATOR contract, and passes keyHash, callbackGasLimit, numWords and refundRecipient as arguments. The payment for service is sent through msg.value to the requestRandomWords() in COORDINATOR contract. If the payment is larger than expected payment, exceeding payment is returned to the refundRecipient address. Eventually, it generates a request for random words. To accurately specify msg.value for the requestRandomWords function, please refer to the explanation on how to estimate the service fee.
Step 4: Fulfill Random Words
The fulfillRandomWords function is called by VRFCoordinator contract when fulfilling the random words request.
function fulfillRandomWords( uint256 /* requestId */, uint256[] memory randomWords) internal override{ // requestId should be checked if it matches the expected request // Generate random value between 1 and 50. sRandomWord = (randomWords[0] % 50) + 1;}
Now that we have the Orakl VRF solution code, let’s get to see it in action.
Practical Implementation
In the example below, the contract allows us to request for random words and receive its fulfillment.
Create and Deploy Sample Code
Remix IDE
- Navigate to Remix IDE.
- Click on the File Explorer tab, create a new file named
consumer-vrf.solin the contracts folder. - Paste the code below in your newly created file.
- In Remix, click Compile contract.
- Click the Kaia tab on your left having installed the plugin.
- Select Environment > Injected Provider - Kaia Wallet.
- In Contract, select your contract. For example,
VRFConsumer. - Pass in the coordinator contract address
0xDA8c0A00A372503aa6EC80f9b29Cc97C454bE499(Kairos),0x3F247f70DC083A2907B8E76635986fd09AA80EFb(Mainnet). - Click Deploy.
Sample Code
// SPDX-License-Identifier: MITpragma solidity ^0.8.16;import {VRFConsumerBase} from "@bisonai/orakl-contracts/src/v0.1/VRFConsumerBase.sol";import {IVRFCoordinator} from "@bisonai/orakl-contracts/src/v0.1/interfaces/IVRFCoordinator.sol";contract VRFConsumer is VRFConsumerBase { uint256 public sRandomWord; address private sOwner; IVRFCoordinator COORDINATOR; error OnlyOwner(address notOwner); modifier onlyOwner() { if (msg.sender != sOwner) { revert OnlyOwner(msg.sender); } _; } constructor(address coordinator) VRFConsumerBase(coordinator) { sOwner = msg.sender; COORDINATOR = IVRFCoordinator(coordinator); } function requestRandomWordsDirect( bytes32 keyHash, uint32 callbackGasLimit, uint32 numWords, address refundRecipient ) public payable onlyOwner returns (uint256 requestId) { requestId = COORDINATOR.requestRandomWords{value: msg.value}( keyHash, callbackGasLimit, numWords, refundRecipient ); } function fulfillRandomWords( uint256 /* requestId */, uint256[] memory randomWords ) internal override { // requestId should be checked if it matches the expected request // Generate random value between 1 and 50. sRandomWord = (randomWords[0] % 50) + 1; }}
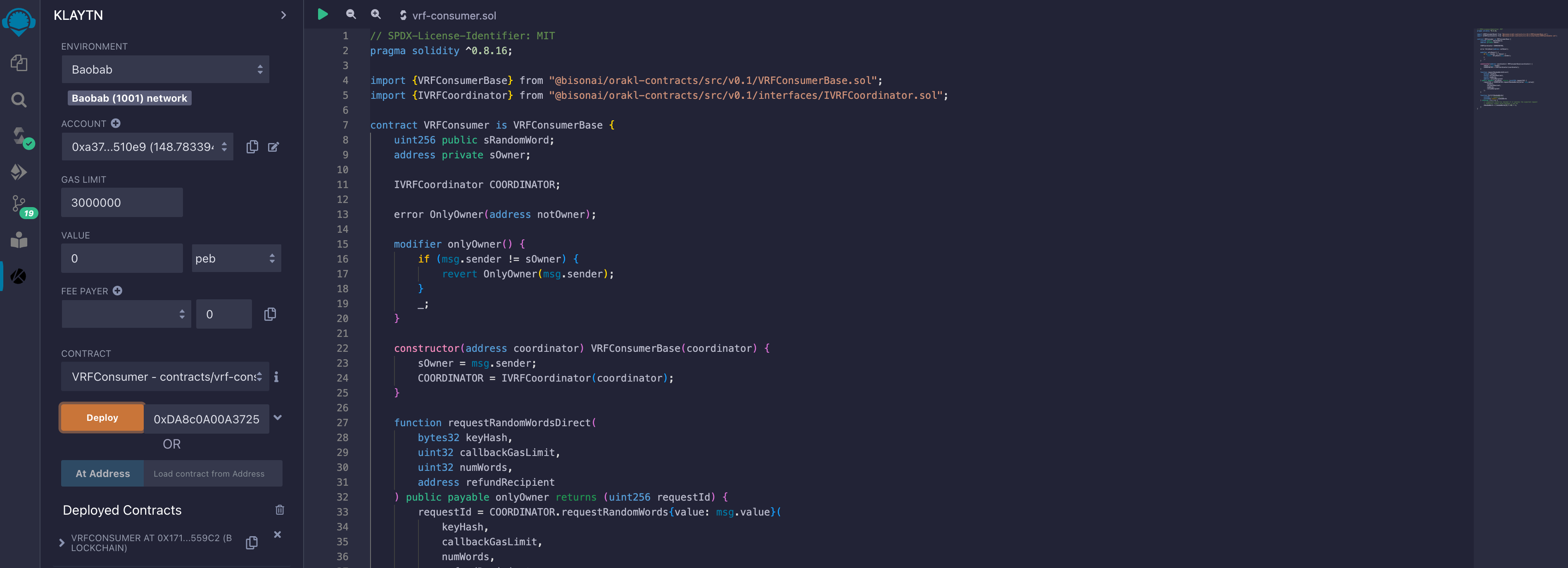
Interact with Smart Contract
To request for random words in your smart contract, you have to first execute the requestRandomWordsDirect() function. For this function to successfully execute, the user has to send KAIA (minimum of 1 KAIA) as stated previously, and supply keyHash, callbackGasLimit, numWords, and refundRecipient parameters. keyHash parameter uniquely defines who can fulfill the request. Orakl Network VRF provides one key hash for each Kaia chain:
- Kairos:
0xd9af33106d664a53cb9946df5cd81a30695f5b72224ee64e798b278af812779c - Mainnet:
0x6cff5233743b3c0321a19ae11ab38ae0ddc7ddfe1e91b162fa8bb657488fb157
For the rest of the parameters, you can set them as follows:
callbackGasLimitas500000,numWordsas1, and- set
refundRecipientto your EOA address.
Afterwards, once the request has been fulfilled, the sRandomWord() function can be executed. This sRandomWord() function returns the random word.
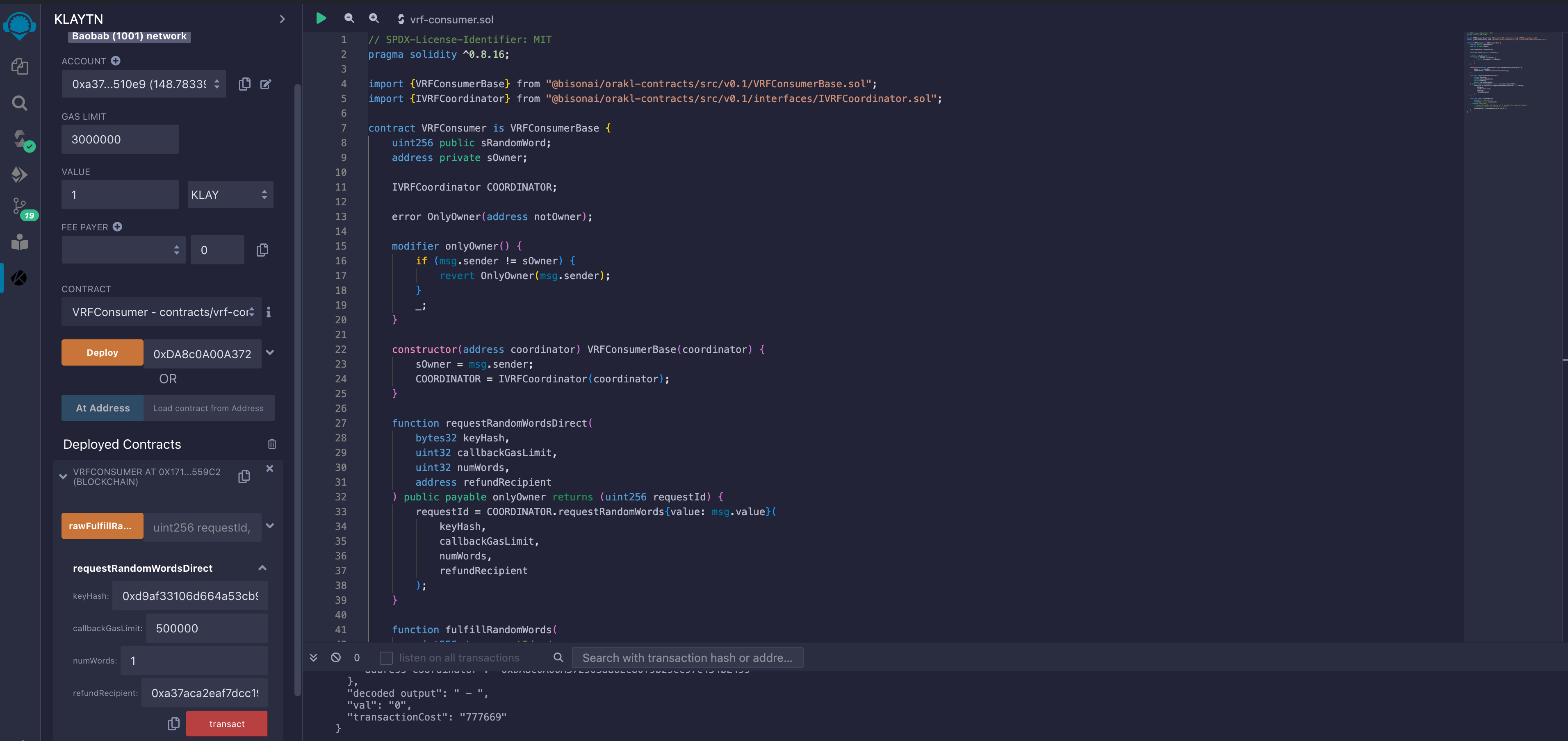
- requestRandomWordsDirect(): Will be sending 1 KAIA to execute this function. The image below illustrate this:
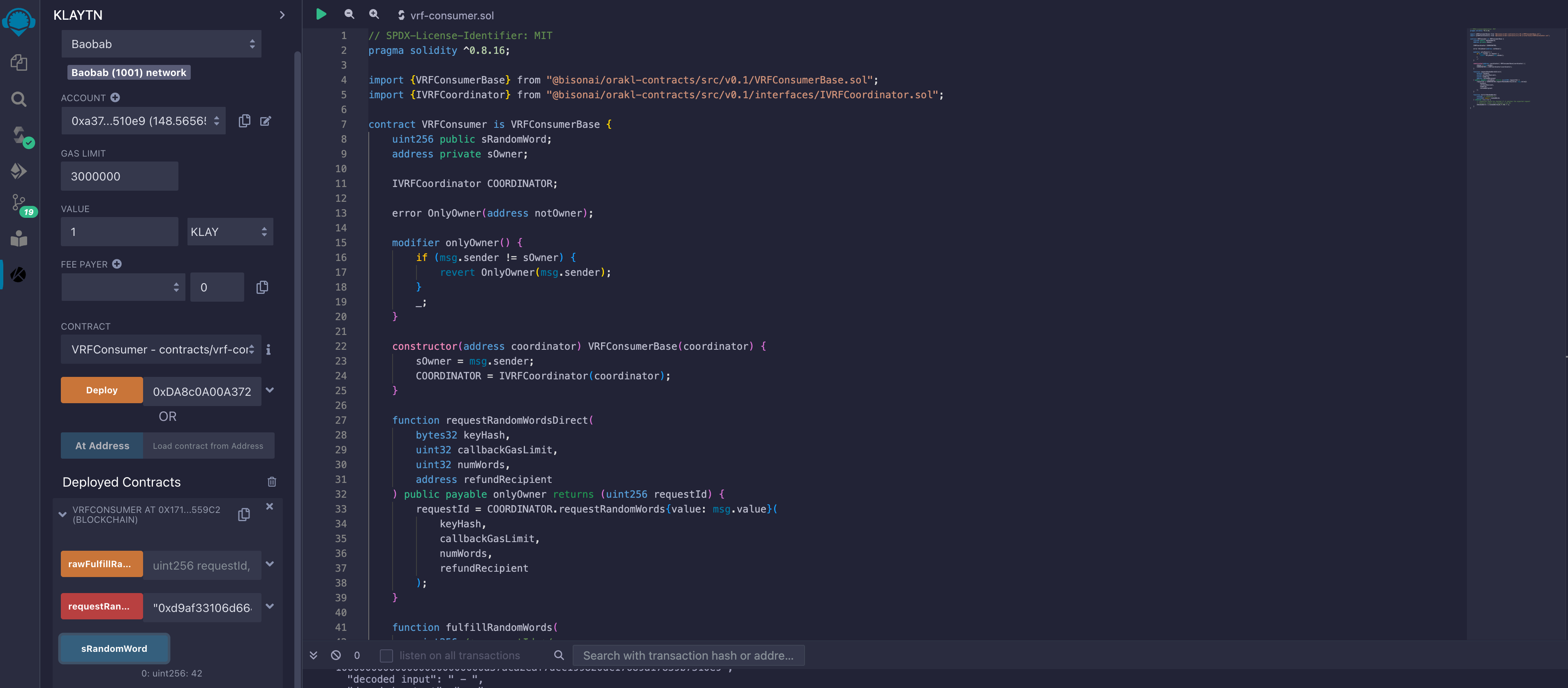
- sRandomWord(): After the
VRFCoordinatorhas fulfilled the random word request, the response is stored in thesRandomWordvariable. To get the response, call thesRandomWord()function.
Tada 🎉! You just requested for a random word and received one in your smart contract.
Conclusion
In this tutorial, you learnt how to generate a random word in your smart contract using the Orakl Network VRF solution. The Orakl Network provides more oracle services such as Data Feed, Request-Response, Proof of Reserve. For more in-depth guides on Orakl Network and how it works, please refer to the Orakl Network documentation.